Learning-Based Multiuser Scheduling in MIMO-OFDM Systems with Hybrid Beamforming
Pouya Agheli, Tugce Kobal, François Durand, and Matthew Andrews
European Conference on Networks and Communications (EuCNC) & 6G Summit
Poznan, Poland
Jun 6, 2025
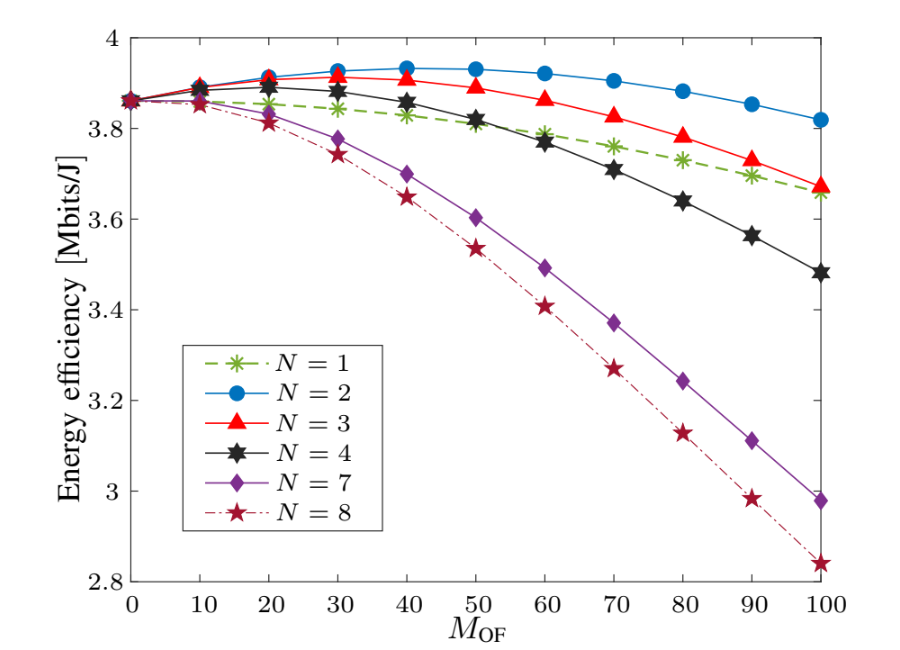
PF vs max. number of users
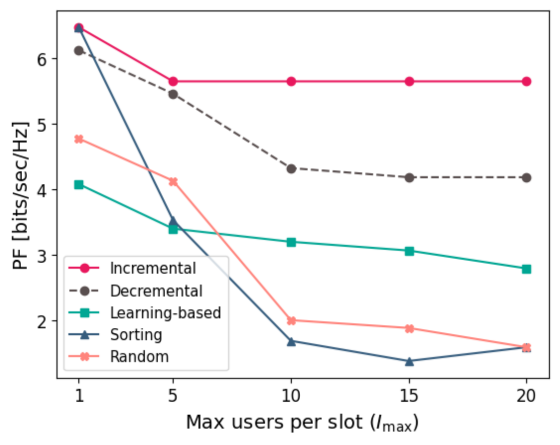
Run time vs max. number of users
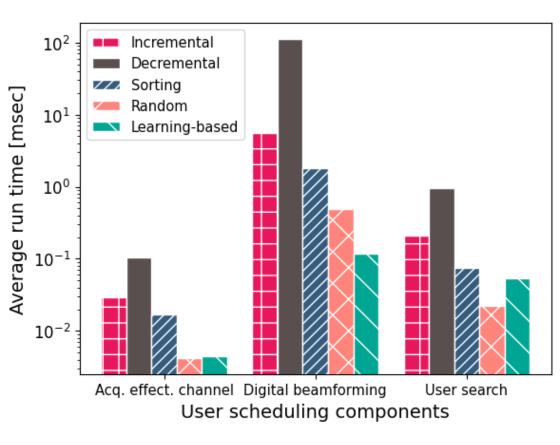
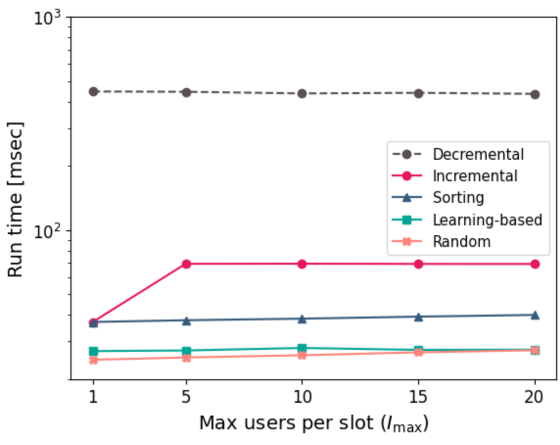
Algos' profiles
Pull-Based Query Scheduling for Goal-Oriented Semantic Communication
Pouya Agheli, Nikolaos Pappas, and Marios Kountouris
Preprint (Submitted for possible IEEE publication)
Mar 9, 2025
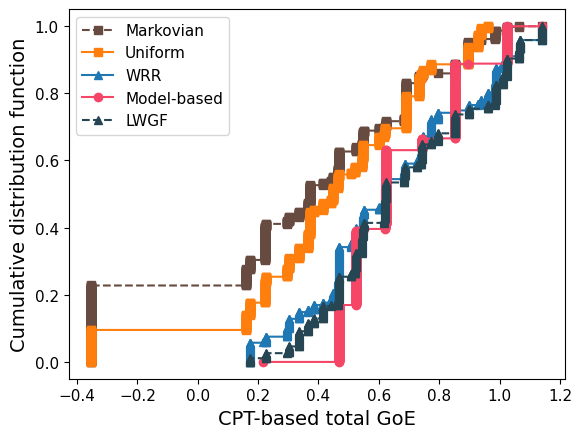
CDF of GoE
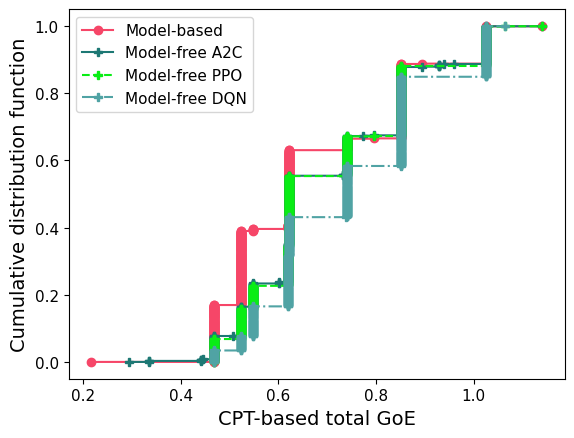
CDF of GoE - DRL
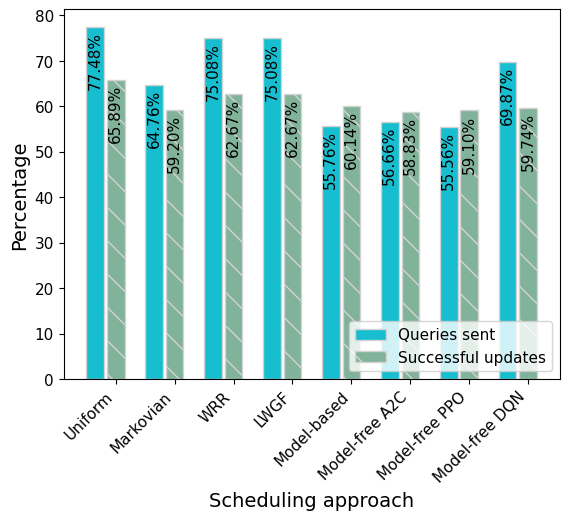
Statistics of queries and actions
Integrated Push-and-Pull Update Model for Goal-Oriented Effective Communication
Pouya Agheli, Nikolaos Pappas, Petar Popovski, and Marios Kountouris
Preprint (Submitted for possible IEEE publication)
Jul 19, 2024
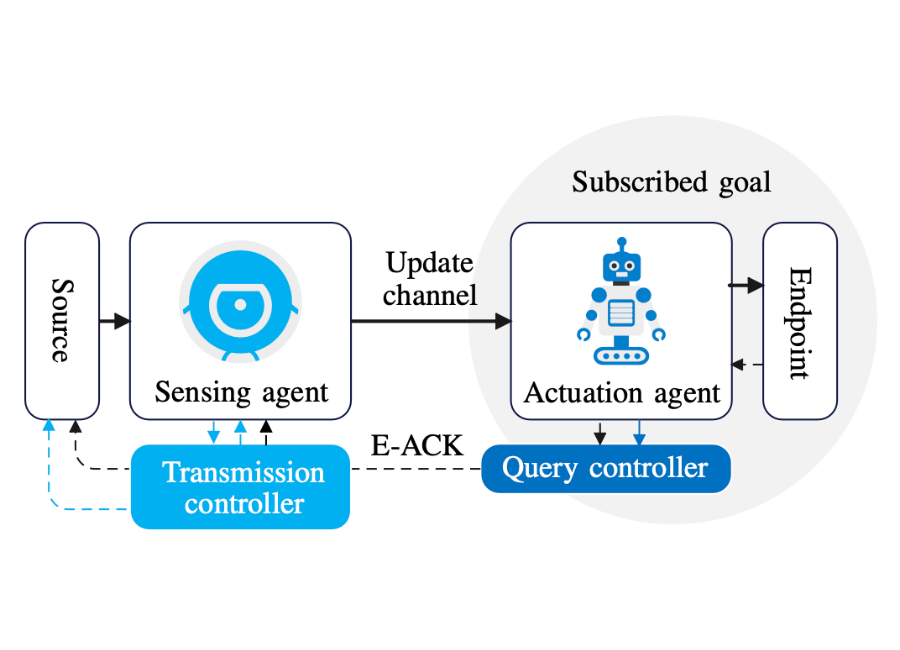
End-to-end status update communication to satisfy a subscribed goal.
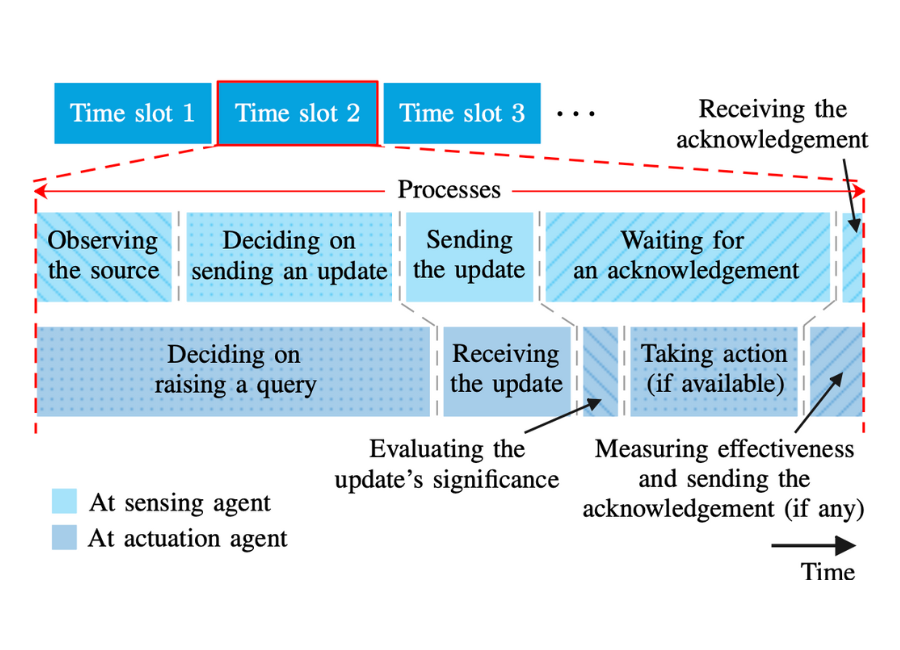
A time diagram of processes involving the sensing and actuation agents
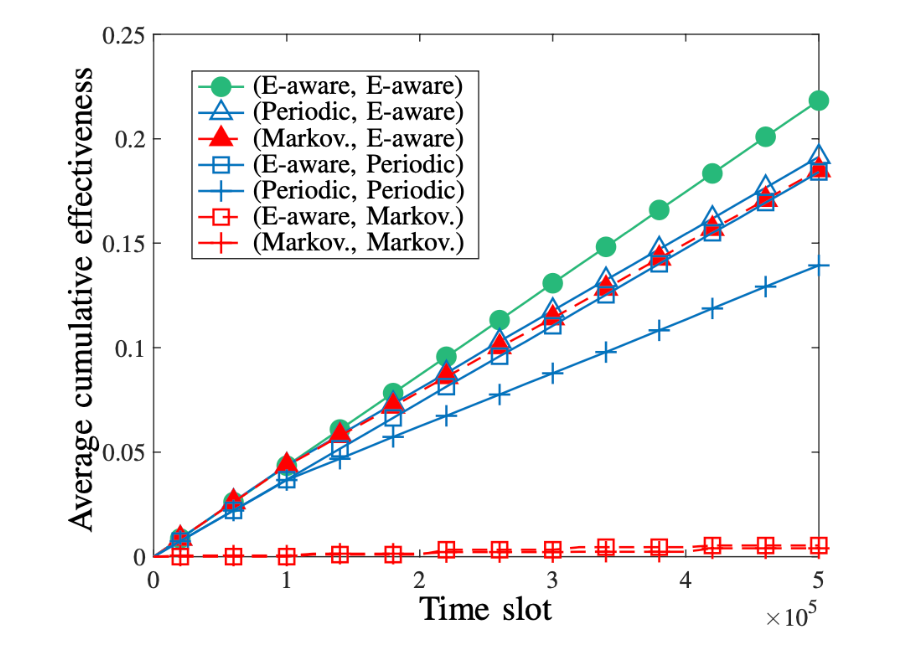
Average cumulative effectiveness over time
Goal-Oriented Multiple Access Connectivity for Networked Intelligent Systems
Pouya Agheli, Nikolaos Pappas, and Marios Kountouris
IEEE Communications Letters (Volume: 28, Issue: 8)
Jun 17, 2024
We design a self-decision goal-oriented multiple access scheme, where sensing agents observe a common event and individually decide to communicate the event’s attributes as updates to the monitoring agents, to satisfy a certain goal. Decisions are based on the usefulness of updates, generated under uniform, change- and semantics-aware acquisition, as well as statistics and updates of other agents.We obtain optimal activation probabilities and threshold criteria for decision-making under all schemes, maximizing a grade of effectiveness metric. Alongside studying the effect of different parameters on effectiveness, our simulation results show that the self-decision scheme may attain at least 92% of optimal performance.
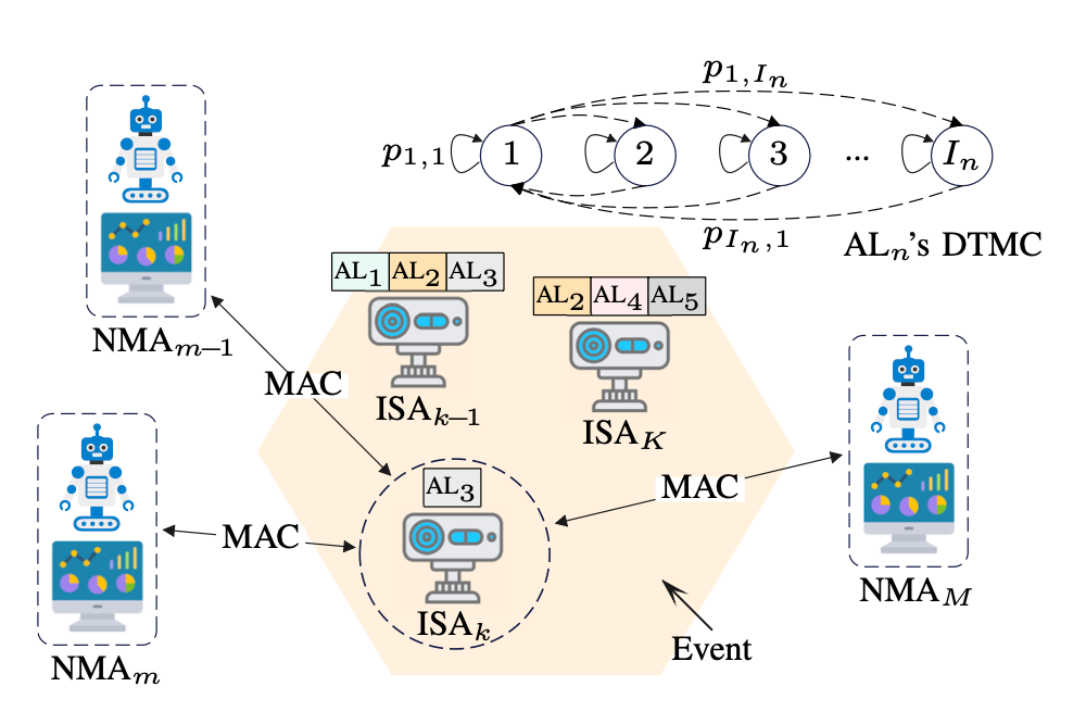
Goal-Oriented Medium Access in a Networked Intelligent System
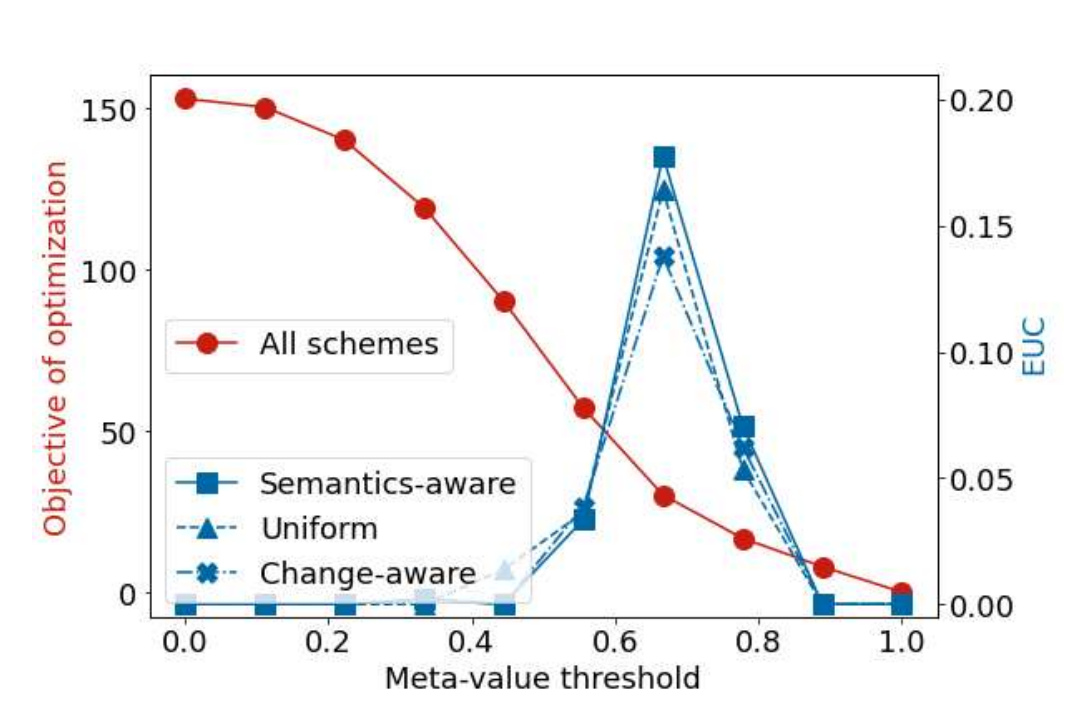
Objective vs. Meta-Value Threshold

Objective vs. Number of the Source' DTMC States
Effective Communication: When to Pull Updates?
Pouya Agheli, Nikolaos Pappas, Petar Popovski, and Marios Kountouris
IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC)
Denver, CO, USA
Jun 10, 2024
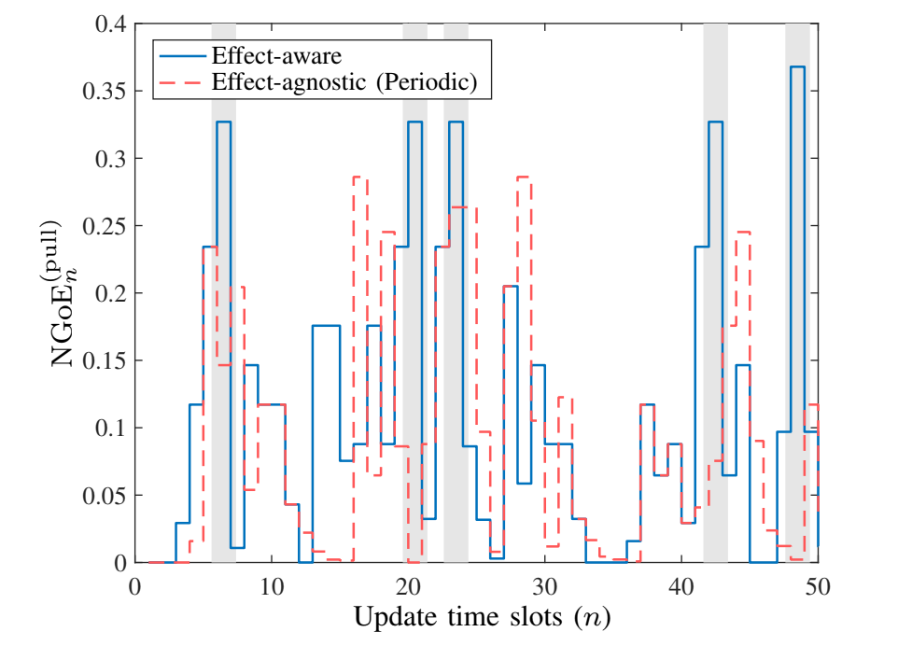
Evolution of the Net GoE (NGoE) over Time
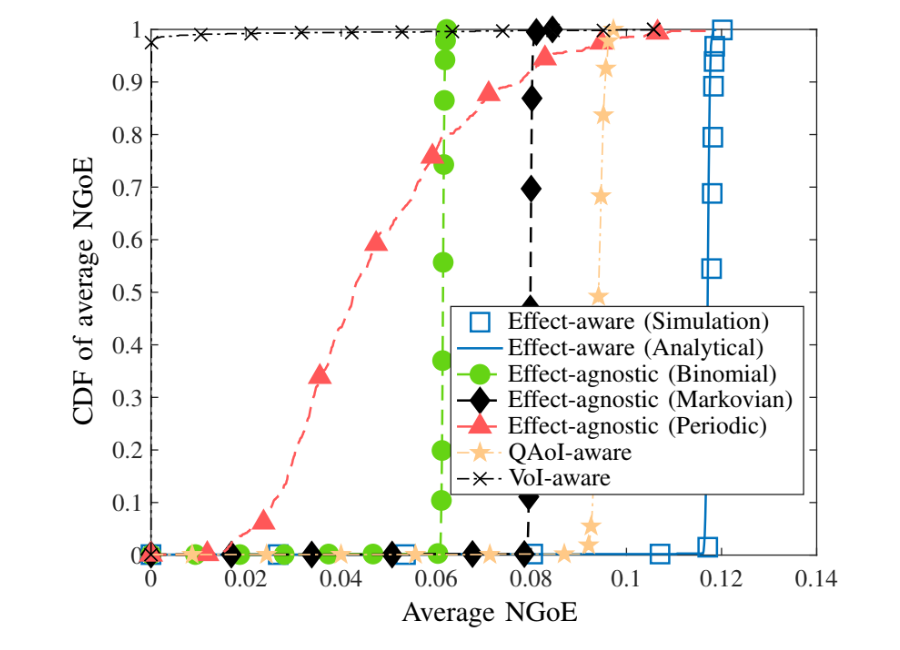
CDF of the Average NGoE
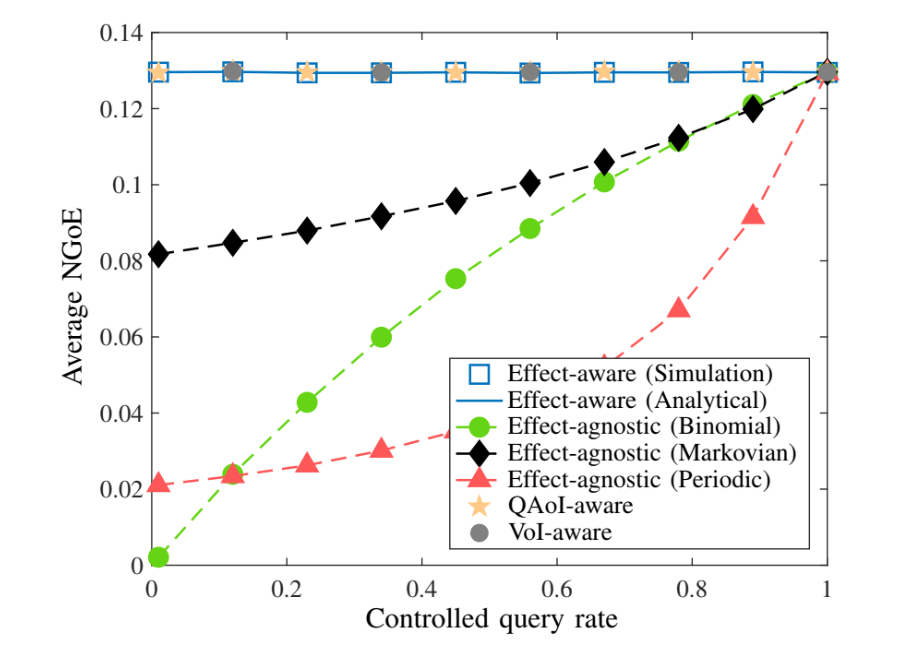
Average NGoE vs. the Controlled Query Rate
Semantic Filtering and Source Coding in Distributed Wireless Monitoring Systems
Pouya Agheli, Nikolaos Pappas, and Marios Kountouris
IEEE Transactions on Communications (Volume: 72, Issue: 6)
Feb 6, 2024
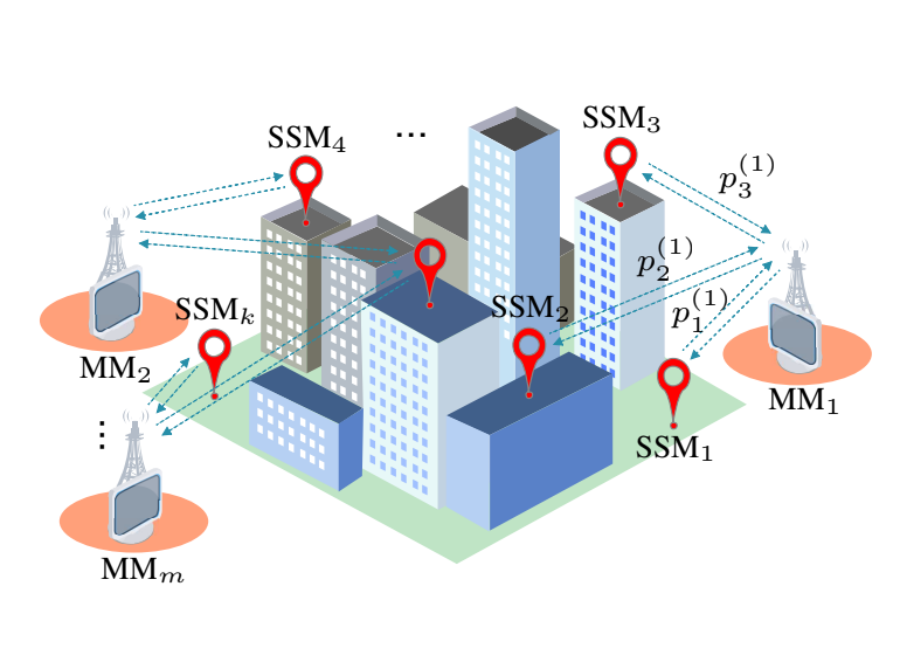
A Goal-Oriented, Semantics-Empowered Distributed Monitoring System
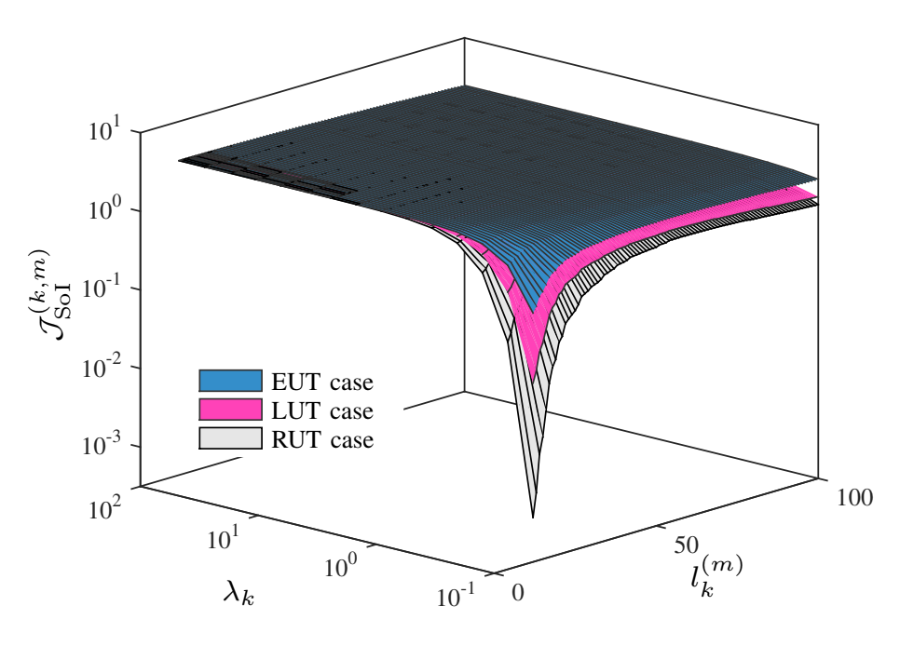
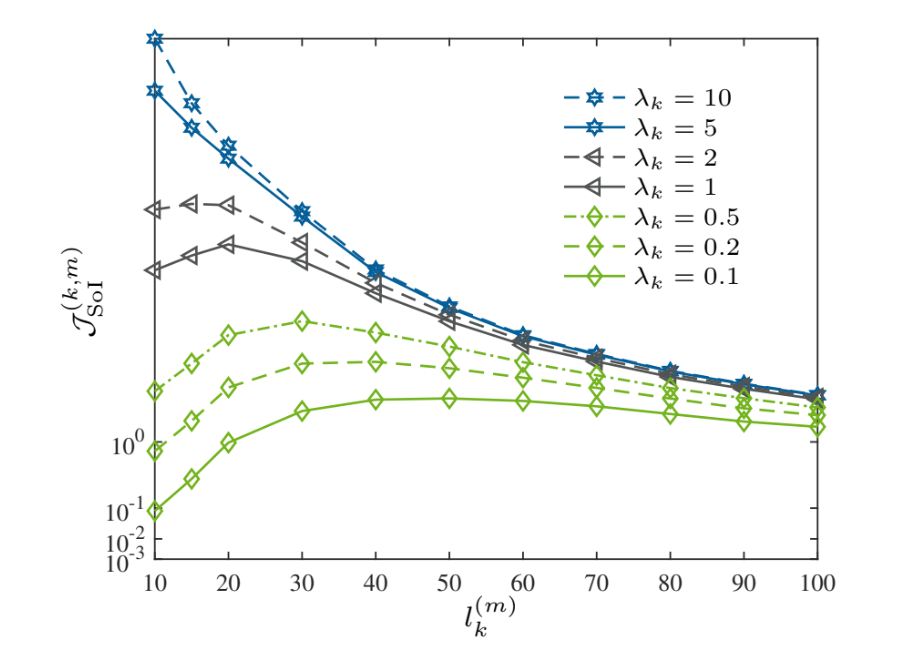
Semantics of Information (SoI) vs. the Arrival Rate and Admission Size
SoI vs. the Admission Size
Semantic Source Coding for Two Users with Heterogeneous Goals
Pouya Agheli, Nikolaos Pappas, and Marios Kountouris
IEEE Global Communications Conference (GLOBECOM)
Rio de Janeiro, Brazil
Jan 11, 2023
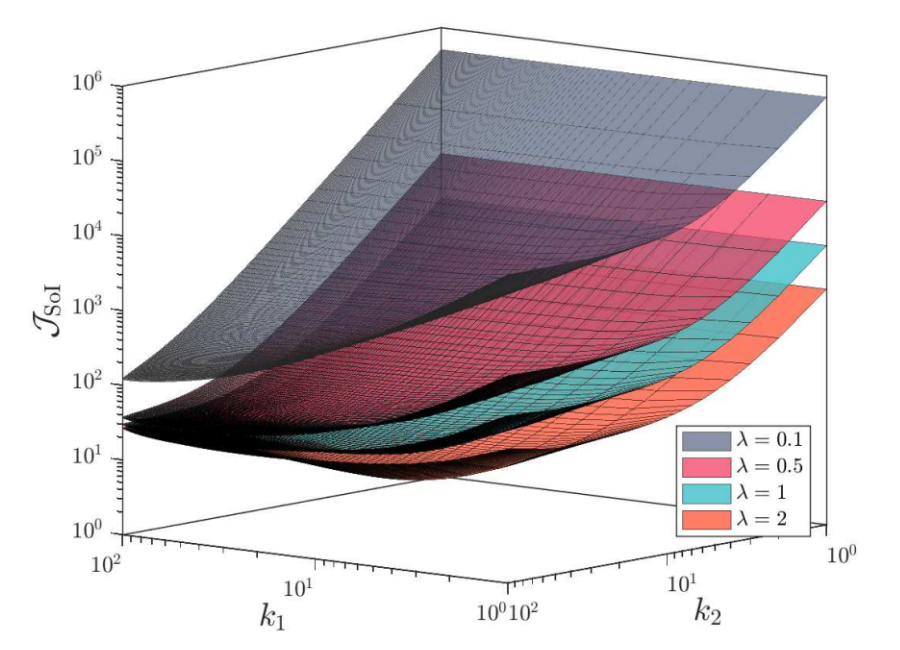
Interplay between the SoI and the Number of Selected Realizations for Different Arrival Rates

Interplay between the SoI and the Number of Selected Realizations for Different Weights
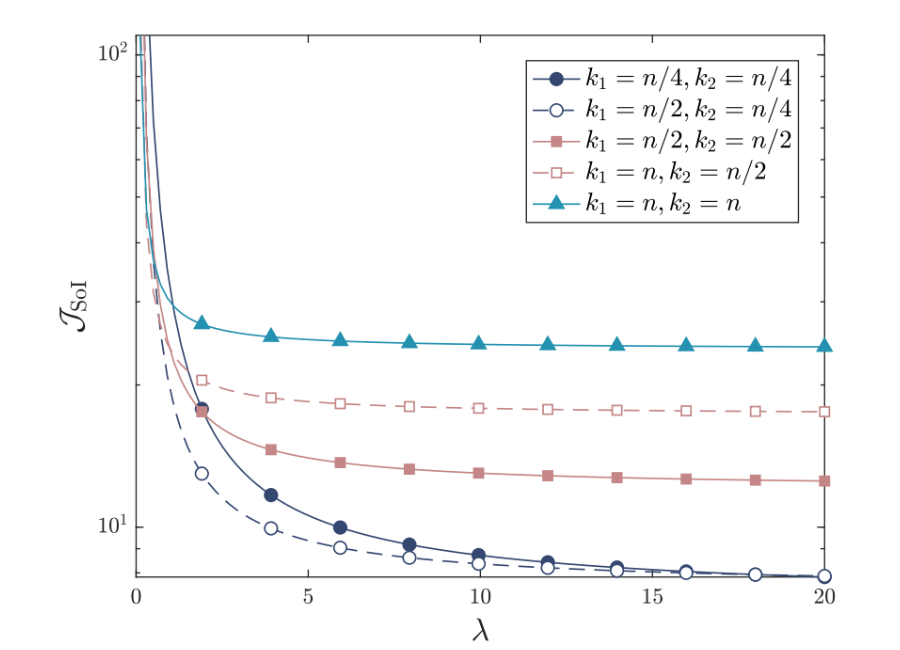
SoI vs. the Arrival Rate
Semantics-Aware Source Coding in Status Update Systems
Pouya Agheli, Nikolaos Pappas, and Marios Kountouris
IEEE International Conference on Communications Workshops (ICC Workshops)
Seoul, Republic of Korea
Jul 11, 2022
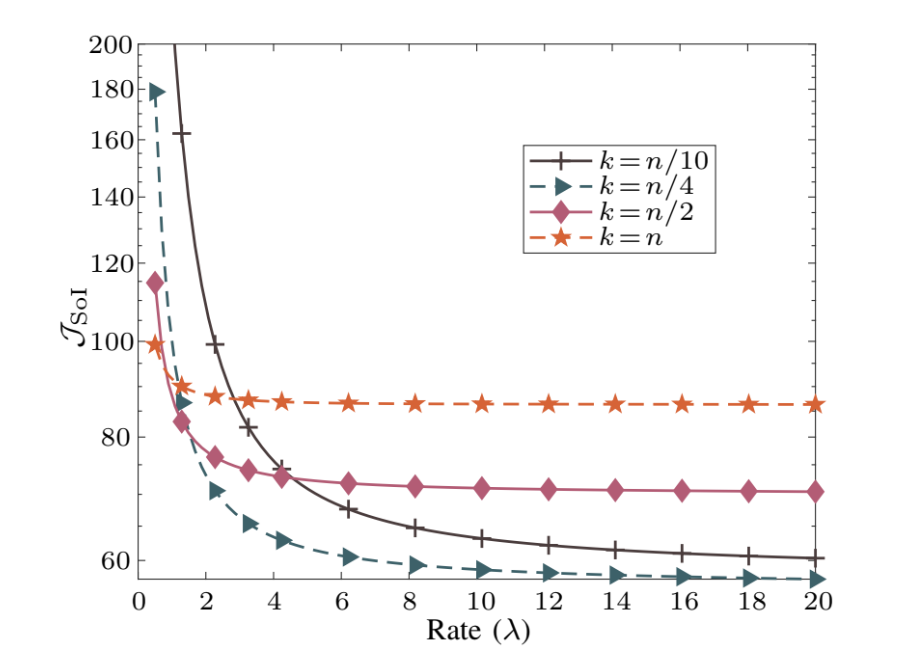
SoI vs. the Arrival Rate for Exponentially Decreasing Timeliness
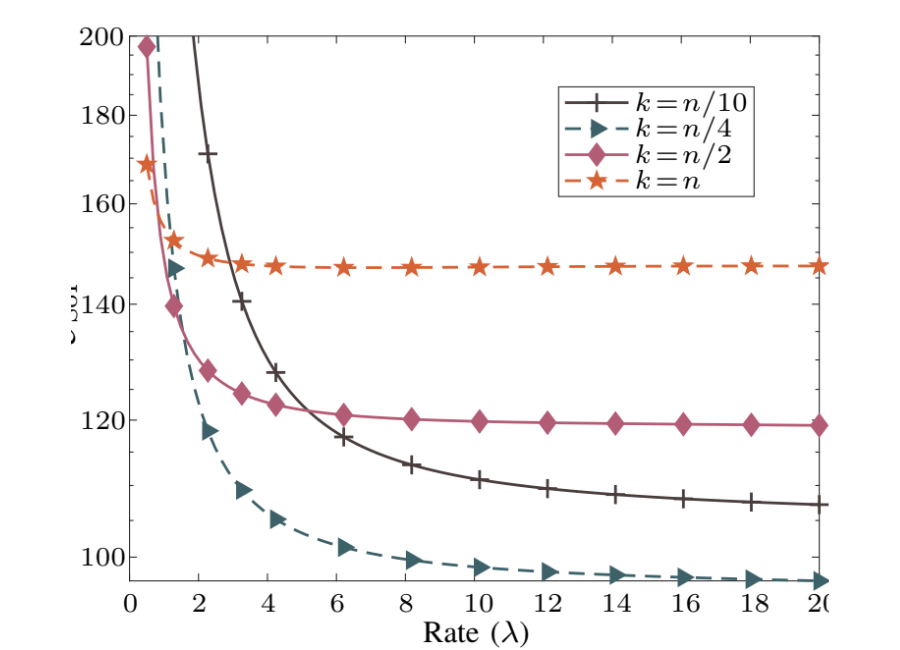
SoI vs. the Arrival Rate for Logarithmically Decreasing Timeliness
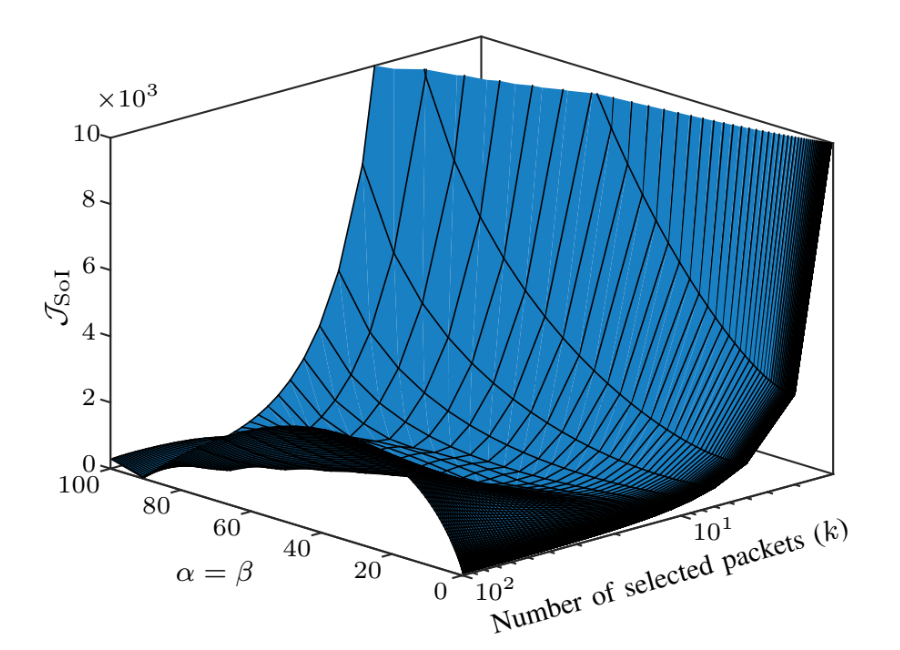
Interplay between the SoI, Selected Packets and Codeword Length Cost Parameters
High-Speed Trains Access Connectivity Through RIS-Assisted FSO Communications
Pouya Agheli, Hamzeh Beyranvand, and Mohammad Javad Emadi
IEEE/OSA Journal of Lightwave Technology (Volume: 40, Issue: 21)
Aug 17, 2022
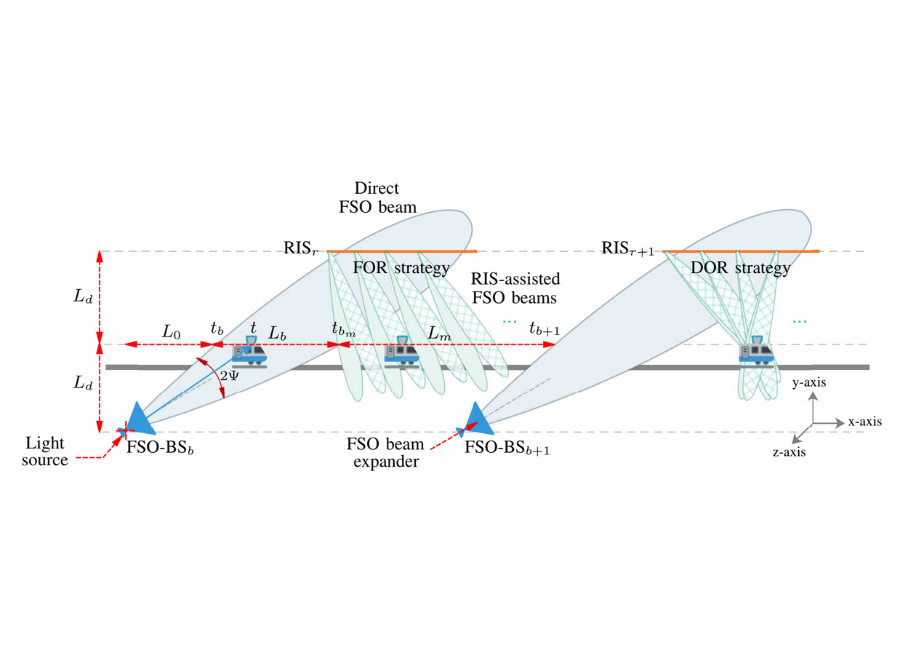
RIS-Assisted FSO Access Network Serving an HST System
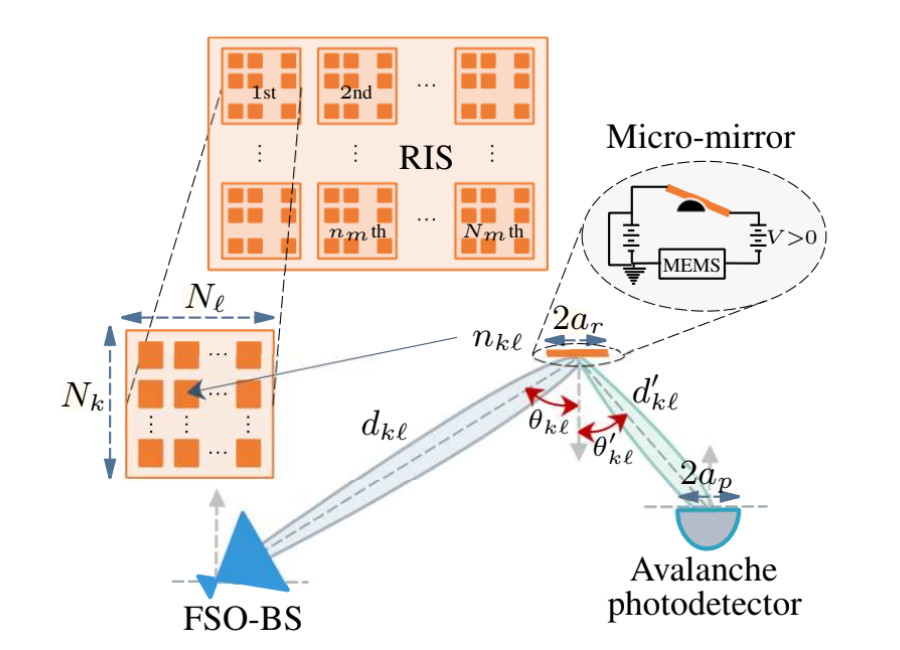
FSO Beam’s Reflection Through a RIS-Assisted Structure
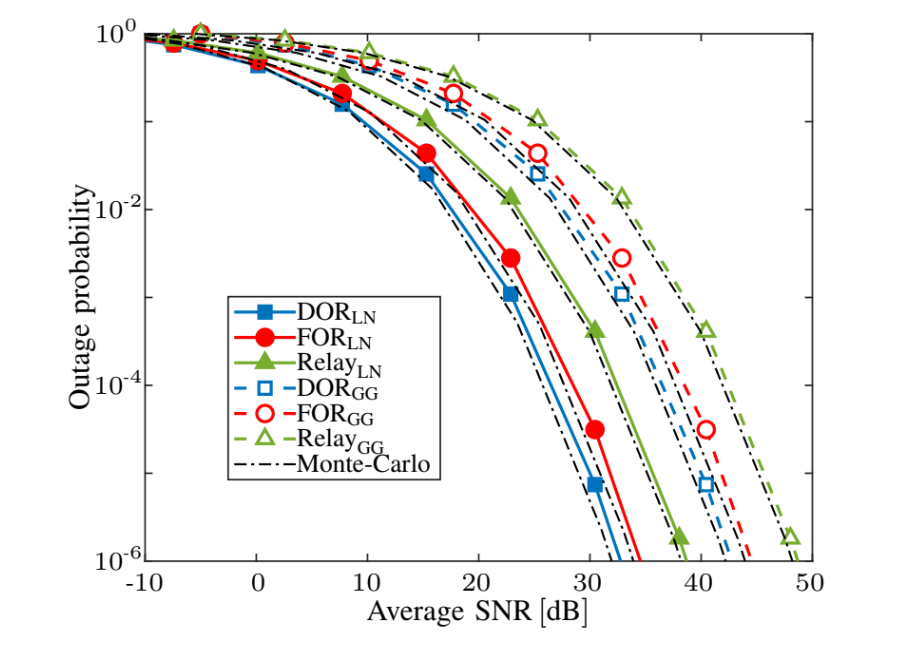
Outage Probability vs. Average SNR
Cognitive RF-FSO Fronthaul Assignment in Cell-Free and User-Centric mMIMO Networks
Pouya Agheli, Mohammad Javad Emadi, and Hamzeh Beyranvand
IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing (Volume: 22, Issue: 5)
Dec 3, 2021
Cell-free massive MIMO (CF-mMIMO) network and its user-centric (UC) version are considered as promising techniques for the next generations of wireless networks. However, fronthaul and backhaul assignments are challenging issues in these networks. In this paper, energy efficiencies of uplink transmission for the CF- and UC-mMIMO networks are studied, wherein access points (APs) are connected to aggregation nodes (ANs) through radio frequency (RF) and/or free-space optic (FSO) fronthauls, and the ANs are connected to a central processing unit via fiber backhauls. The achievable data rates are derived by taking into account the effects of hardware non-ideality at the APs and ANs, FSO alignment and weather conditions. To have a robust and energy-efficient network, especially in the presence of FSO misalignment and adverse weather conditions, first, a cognitive RF–FSO fronthaul assignment algorithm is proposed at the cost of sharing the available RF bandwidth between the access and fronthaul links. Then, optimal power allocations at the users and APs are investigated, and two analytical approaches are proposed to solve the non-convex optimization problem. Through numerical results, we have discussed how utilizing the cognitive RF–FSO fronthaul assignment achieves higher energy efficiency compared to that of FSO-only, RF-only, or simultaneously using RF and FSO fronthaul links, e.g., achieving up to 198% higher energy efficiency under unfavorable conditions. Moreover, the effects of FSO misalignment, weather conditions, and power allocations on the networks’ performances are discussed.
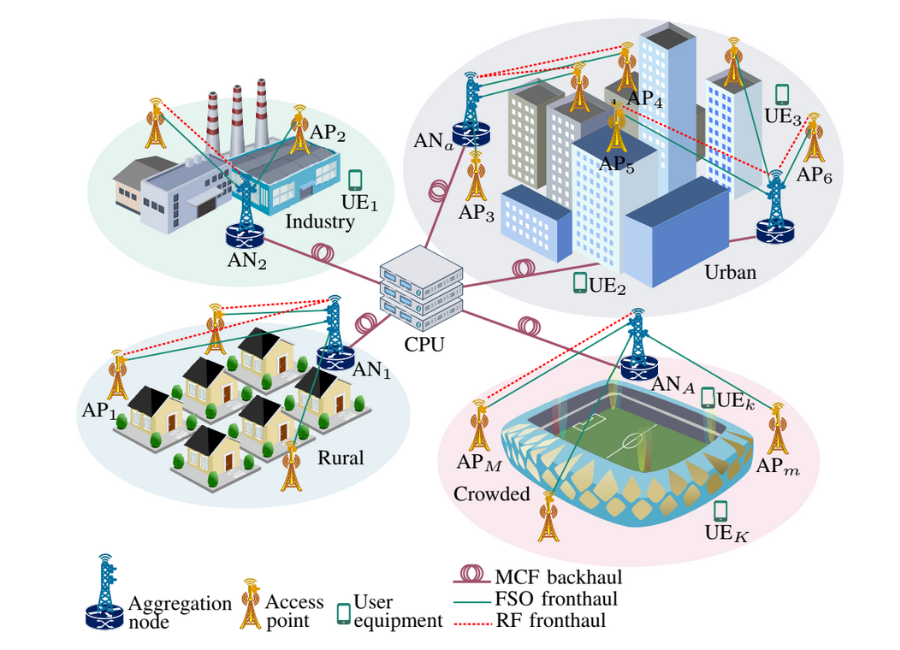
Massive MIMO Network with RF–FSO Fronthauls and MCF Backhauls
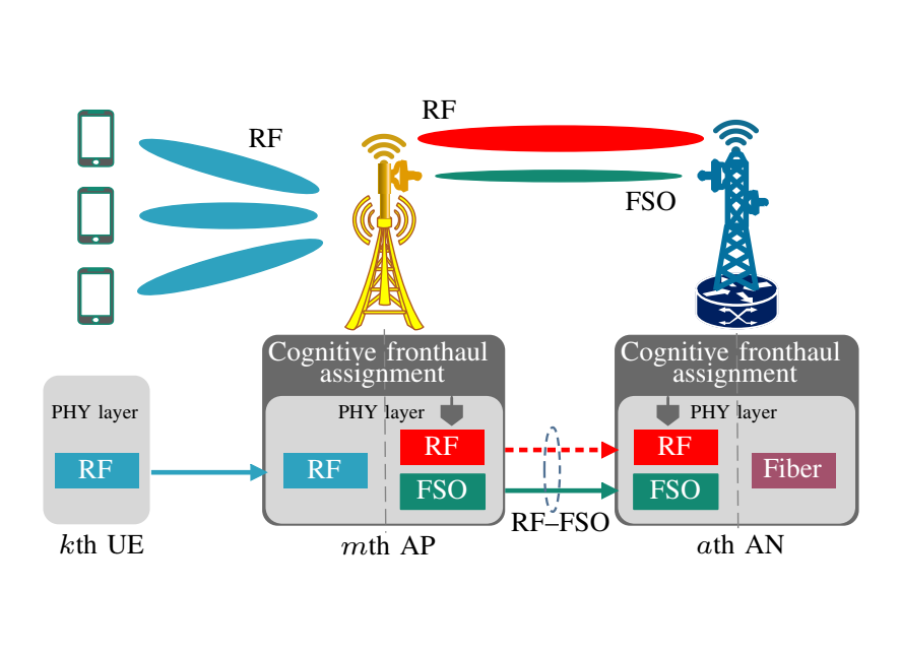
Signal Flow over Access and Cognitively-Assigned Fronthaul Links
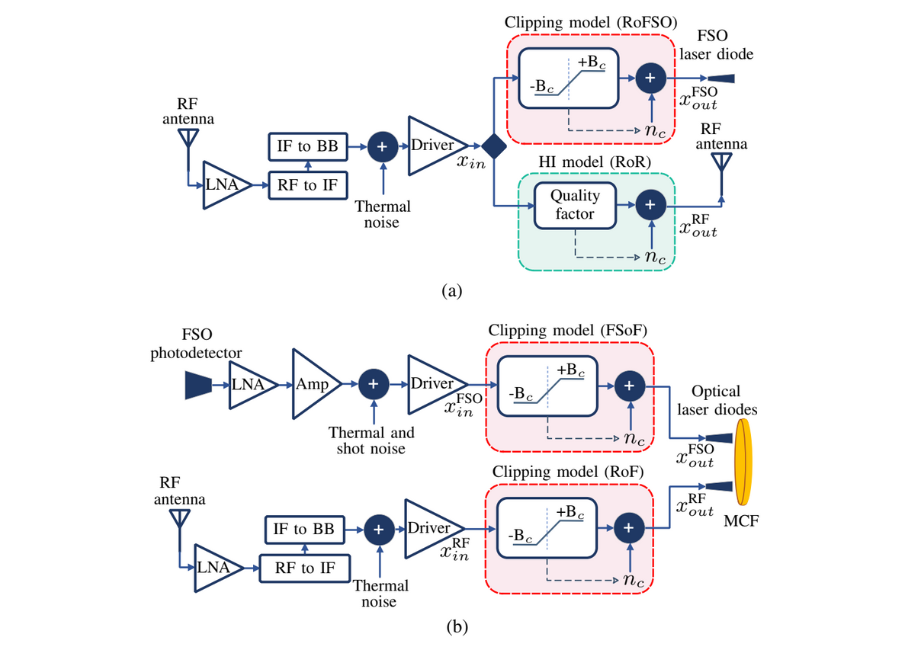
Simplified Hardware Models at the (a) APs and (b) ANs
UAV-Assisted Underwater Sensor Networks Using RF and Optical Wireless Links
Pouya Agheli, Mohammad Javad Emadi, and Hamzeh Beyranvand
IEEE/OSA Journal of Lightwave Technology (Volume: 39, Issue: 22)
Sep 21, 2021
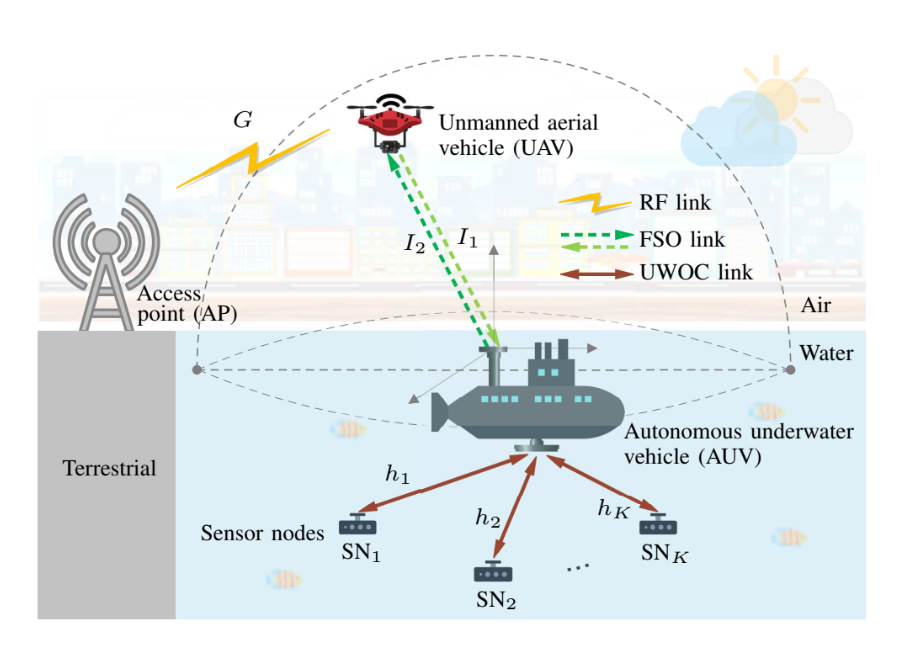
UAV-Assisted UWSN with RF and Optical Wireless Links
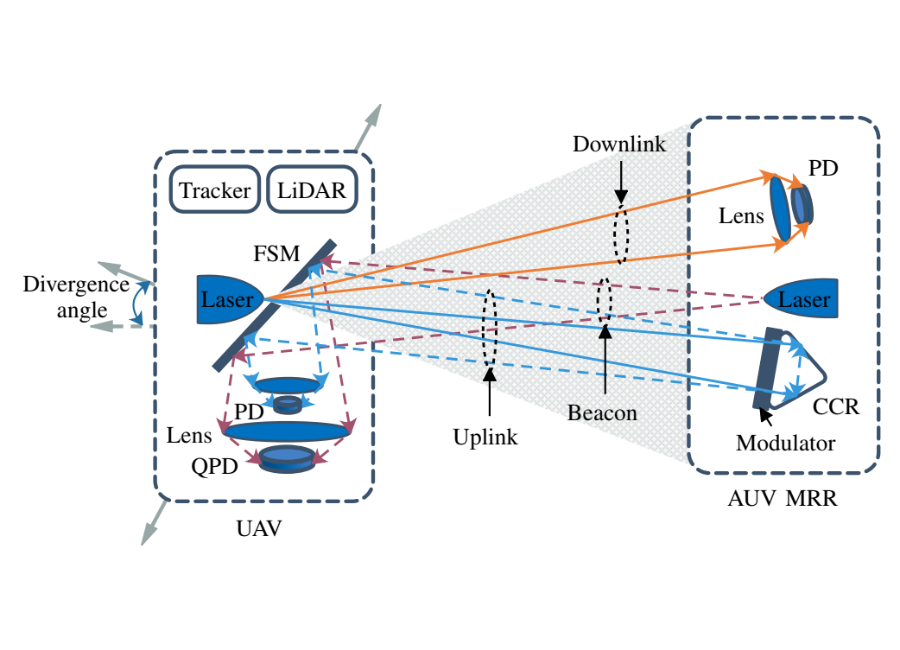
Retro-Reflection System between the AUV and UAV Relays
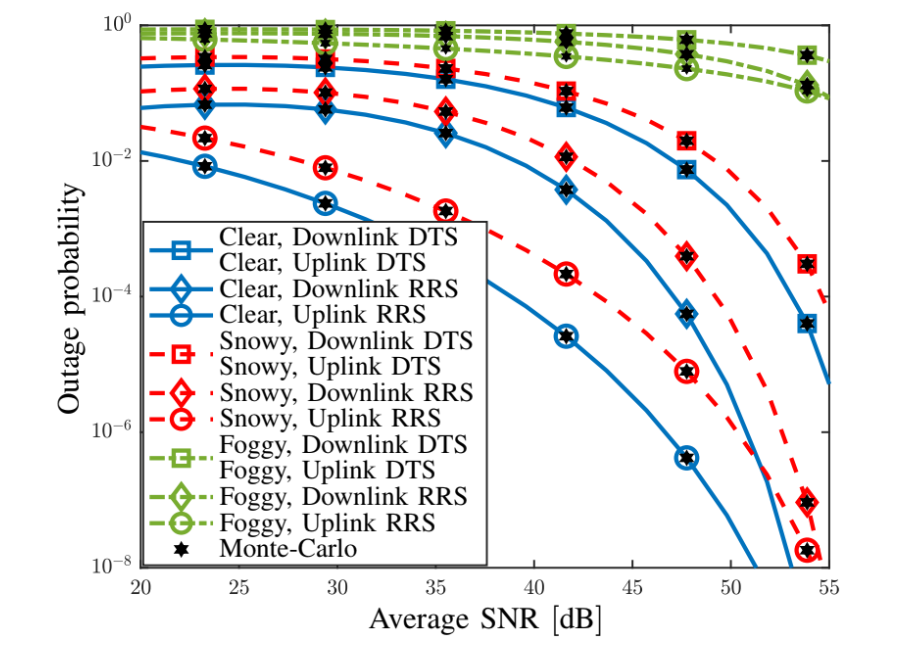
Outage Probability vs. Average SNR
Designing Cost- and Energy-Efficient Cell-Free Massive MIMO Network with Fiber and FSO Fronthaul Links
Pouya Agheli, Mohammad Javad Emadi, and Hamzeh Beyranvand
AUT Journal of Electrical Engineering (Volume: 53, Issue: 2)
Feb 3, 2021

CF-mMIMO Wireless Network with Fiber and FSO Fronthaul Links
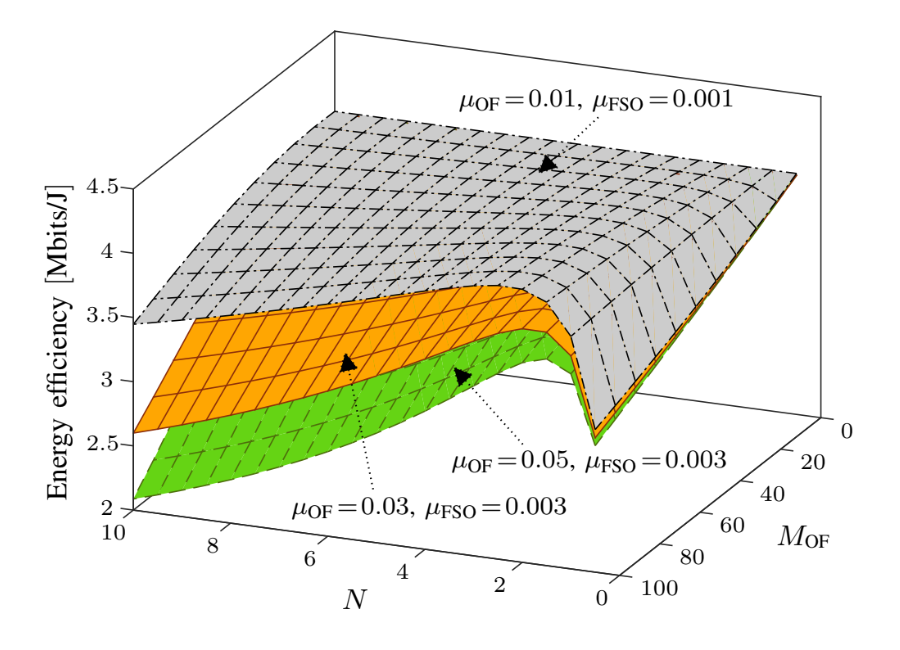
Impact of Cost Parameters on Energy Efficiency